In November 2014, the Wall Street Journal reported that the Bank of North Dakota (BND), the nation’s only state-owned bank, “is more profitable than Goldman Sachs Group Inc., has a better credit rating than JPMorgan Chase & Co. and hasn’t seen profit growth drop since 2003.” The article credited the shale oil boom; but as discussed earlier here, North Dakota was already reporting record profits in the spring of 2009, when every other state was in the red and the oil boom had not yet hit. The later increase in state deposits cannot explain the bank’s stellar record either.
Then what does explain it? The BND turns a tidy profit year after year because it has substantially lower costs and risks then private commercial banks. It has no exorbitantly-paid executives; pays no bonuses, fees, or commissions; has no private shareholders; and has low borrowing costs. It does not need to advertise for depositors (it has a captive deposit base in the state itself) or for borrowers (it is a wholesome wholesale bank that partners with local banks that have located borrowers). The BND also has no losses from derivative trades gone wrong. It engages in old-fashioned conservative banking and does not speculate in derivatives.
Lest there be any doubt about the greater profitability of the public banking model, however, this conclusion was confirmed in January 2015 in a report by the Savings Banks Foundation for International Cooperation (SBFIC) (the Sparkassenstiftung für internationale Kooperation), a non-profit organization founded by the the Sparkassen Finance Group (Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe) in Germany. The SBFIC was formed in 1992 to make the experience of the German Sparkassen—municipally-owned savings banks—accessible in other countries.
The Sparkassen were instituted in the late 18th century as nonprofit organizations to aid the poor. The intent was to help people with low incomes save small sums of money, and to support business start-ups. Today, about half the total assets of the German banking system are in the public sector. (Another substantial chunk is in cooperative savings banks.) Local public banks are key tools of German industrial policy, specializing in loans to the Mittelstand, the small-to-medium size businesses that are at the core of that country’s export engine. The savings banks operate a network of over 15,600 branches and offices and employ over 250,000 people, and they have a strong record of investing wisely in local businesses.
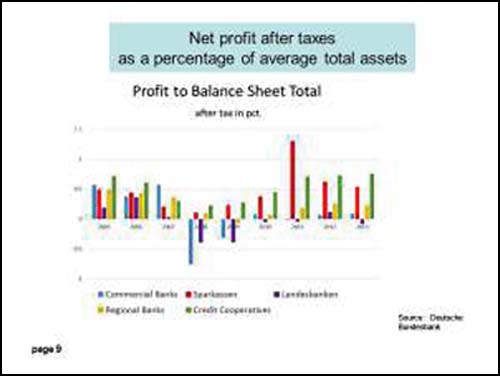
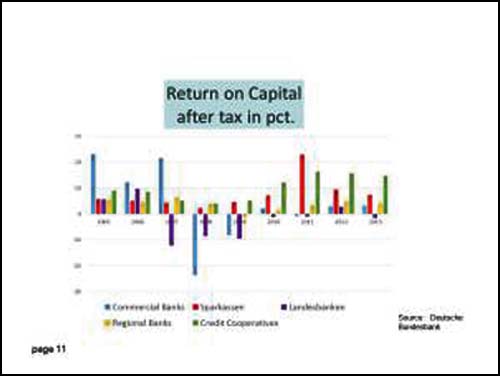
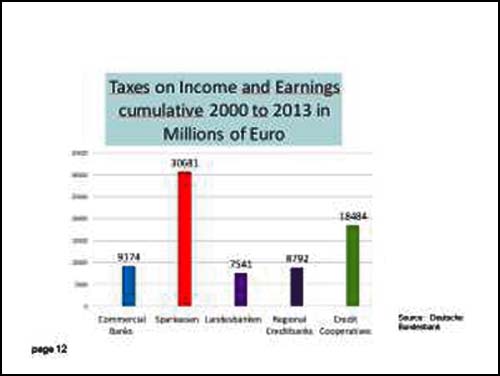
In January 2015, the SPFIC published a report drawn from Bundesbank data, showing that the Sparkassen not only have a return on capital that is several times greater than for the German private banking sector, but that they pay substantially more to local and federal governments in taxes. That makes them triply profitable: as revenue-generating assets for their government owners, as lucrative sources of taxes, and as a stable funding mechanism for small and medium-sized businesses (a funding mechanism sorely lacking in the US today). Three charts from the SBFIC report are reproduced in English below. (Sparkassen results are in orange. Private commercial banks are in light blue.)
Swiss publicly-owned banks and the Swiss National Bank: Marching to a different drummer
The Swiss have a network of cantonal (provincially-owned) banks that are so similar to the Sparkassen banks that they were invited to join the SBFIC. The Swiss public banks, too, have been shown to be more profitable than their private counterparts. The Swiss public banking system helps explain the strength of the Swiss economy, the soundness of its banks, and their attractiveness as a safe haven for foreign investors.
The unique structure of the Swiss banking system also helps explain the surprise move by the SNB on January 15, 2015, when it lifted the cap on the Swiss franc as against the euro, anticipating the European Central Bank’s move to embark on a massive program of quantitative easing the following week. Switzerland is not a member of the EU or the Eurozone, and the Swiss National Bank (SNB) is not like other central banks. It is 55% owned by the country’s 26 cantons or provinces. The remaining investors are private. Each canton has its own publicly-owned cantonal bank, which provides credit to local small and medium-sized businesses.
In 2011, the SNB pegged the Swiss franc to the euro at 1 to 1.20; but the value of the euro steadily dropped after that, and the SNB could maintain the peg only by printing Swiss francs, diluting their value to keep up with the euro. The fear was that once the ECB started its new money printing program, the Swiss franc would have to be diluted into hyperinflation to keep up.
The SNB’s unanticipated action imposed heavy losses on speculators who were long the euro (betting it would rise), and the move evoked criticism from the European central banking community for not tipping them off beforehand. But the loyalty of the Swiss National Bank is to its cantons, cantonal banks, and individual investors, not to the big private international banks that drive central bank policies in other countries. The cantons had been complaining that they were no longer receiving the hefty 6% dividend they had been able to count on for the previous century. The SNB promised to restore the dividend in 2015, and lifting the cap was evidently felt necessary to do it.
Publicly-owned banks and the Trans-Pacific Partnership
The SBFIC is working particularly hard these days to make information and technical help available to other countries interested in pursuing their beneficial public model, because that model has come under attack. Private international competitors are pushing for regulations that would limit the advantages of publicly-owned banks, through Basel III, the European Banking Union, and the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP).
In the US, the current threat is from the TransPacific Partnership (TPP) and its European counterpart the TTIP. President Obama, the Chamber of Commerce, and other corporate groups are pushing hard for fast track authority to pass these secret trade agreements while effectively bypassing oversight from Congress.
The agreements are being sold as promoting trade and increasing jobs, but the effect of international trade agreements on jobs was evident with NAFTA, which hurt US employment more through the competition of cheap imports than helped it with increased exports. Moreover, only five of the TPP’s twenty-nine chapters are about trade. The remaining chapters are basically about getting government off the backs of the big international corporations and protecting their profits from competition. Corporations would be authorized to sue governments that passed laws protecting their people from corporate damage, on the ground that the laws impair corporate profits. The trade agreements put corporations before governments and the people they represent.
Particularly targeted are government-owned industries, which can undercut big corporate prices; and that includes publicly-owned banks. Public banks are true non-profits that recycle earnings back into the community rather than siphoning them into offshore tax havens. Not only are the costs of public banks quite low, but they are safer for depositors; they allow public infrastructure costs to be cut in half (since the government-owned bank can keep the interest that composes 50% of infrastructure costs); and they provide a non-criminal alternative to an international banking cartel caught in a laundry list of frauds.
Despite these notable benefits, under the TPP and TTIP, publicly-owned banks might wind up getting sued for unfair competition because they have advantages not available to private banks, including the backing of their local governments. They have the backing of the government because they are the government. The government would be getting sued for operating efficiently in the best interests of its constituents.
To truly eliminate unfair competition, the giant monopolistic multinational corporations should be broken up, since they have an obvious unfair trade advantage over small farmers and small businesses. But that outcome is liable to be long in coming. In the meantime, fast track for the secretive trade agreements needs to be vigorously opposed. To find out how you can help, go to www.StopFastTrack.com or www.FlushtheTPP.org.
Ellen Brown is an attorney, founder of the Public Banking Institute, and author of twelve books including the best-selling Web of Debt. Her latest book, The Public Bank Solution, explores successful public banking models historically and globally. Her 200+ blog articles are at EllenBrown.com.